How Are Differences in Properties Among the Transition Elements Explained
Explain how a metal can become a temporary magnet. This creates an effective shield between the nucleus and the outer 4s shell.

An Introduction To Qualitative Analysis Transition Element Transition Metal Chemistry
The paramagnetic character of the transition metals increases on moving from left to right as the number of unpaired electron increases from one to five.

. High melting point group 1 metals have low melting points hard group 1 metals are soft high density group 1 metals have lower densities Chemical properties. The general properties of. Thus Sc is a rather active metal whereas Cu is much less reactive.
The definition of transition metals and an explanation of their electron configurations can be found on the transition metals page. The properties of the elements of the first transition series differ from those of the heavier transition elements in many ways. They are frequently paramagnetic.
They usually combine to form coloured compounds. Group 1 metals are also known as alkali metals because these elements can form alkaline compounds. This articles discusses the chemical properties of Vanadium V only.
They form coloured ions and compounds and this can be explained due to the d-d transition in electrons. They exhibit a wide range of oxidation states or positively charged forms. This happens as each additional electron enters the penultimate 3d shell.
They have a low energy gap between the oxidation states of the elements. Compared to other metals most transition metals have. The transition elements have low ionization energies.
The peripheral shell configuration of these elements is ns 2. High density and hardness. This page looks at the uses of transition metals and covers their uses as metals compounds and catalysts.
Similarly from top to bottom elements decrease in electronegativity due to an increasing distance between valence electrons and the nucleus. They are typically metals with a high melting point. The middle elements are found to possess the maximum paramagnetic property.
The d electrons are loosely bound which contributes to the high electrical conductivity and malleability of the transition elements. The paramagnetic character of the transition metals increases on moving from left to right as the number of unpaired electron increases from one to five. Transition metals are the d -block elements and they have incompletely filled d -orbitals.
Among these most are metals and there is less number of nonmetal elements in the p block. Properties of transition elements at room tempertature. The unpaired electrons in n-1 d orbitals are responsible for the magnetic properties.
October 6 2020 Posted by Madhu. Properties of Transition Elements. Most compounds of transition metals are paramagnetic whereas virtually all compounds of the p-block elements are diamagnetic.
Use as metals The properties of transition metals are very similar to the properties of normal metals so Im. Most compounds of transition metals are paramagnetic whereas virtually all compounds of the p-block elements are diamagnetic. The transition elements general properties are as follows.
They have a variety of oxidation states. Vanadium atomic number 23 is a typical transition metal the transition metals are. The elements in the periodic table can be divided mainly into two.
These elements express many oxidation states. From top to bottom each successive element has a lower ionization energy because it is easier to remove an electron since the atoms are less tightly bound. However the atom sizes of the elements in the third transition series are virtually the same as those of.
The electronegativities of the first-row transition metals increase smoothly from Sc χ 14 to Cu χ 19. The unpaired electrons in n-1 d orbitals are responsible for the magnetic properties of these elements. Explain why some metals can act as permanent magnets.
Transition elements are ALL solid metals except for mercury 80Hg which is a liquid. Thus Sc is a rather active metal whereas Cu is much less reactive. The d10 metals namely Zn Cd and Hg have completely filled d -orbitals.
However group 1 of the periodic table contains. How are differences in properties among the transition elements explained. On the periodic table main group elements are found in groups 1 2 and 13-18 while transition metals are found in groups 3-12.
I The atomic sizes of the elements of the first transition series are smaller than those of the heavier elements of 2nd and 3rd transition series. Identify three ways transition metals are separated from their ores. As metals and nonmetals.
Most of the transition elements show paramagnetic behaviour. Transition Metals vs Metals. All transition elements exhibit similar properties because of the identical electronic configuration of their peripheral shell.
The key difference between group 1 metals and transition metals is that group 1 metals form colourless compounds whereas transition metals form colourful compounds. However they are also considered as transition metals because they have similar properties to those of transition metals. In other words they have d1 to d9 electrons.
The physical properties of this element can be found easily in any standard Chemistry textbook. The properties of transition elements are as follows. We know that electronic configurations of transition elements is invariably n-1d 110 ns 0 or 1 or 2 which indicates that i the electronic configurations of transition elements differ from one another only in the number of electrons in d orbitals in the n-1th shell and ii the number of electrons in the outermost shell ns is invariably 1 or 2.
They have a high chargeradius ratio. The three main differences are. The positive oxidation states allow transition elements to form many different ionic and partially.
Some properties of transition elements are different from those of the metals in group 1. How can a transition metal form an ion with a charge of 3 or higher. The electronegativities of the first-row transition metals increase smoothly from Sc χ 14 to Cu χ 19.
Transition Metals Ck 12 Foundation

Use This As A Pattern For Your Own Summary Page On Transition Elements Transition Element Precipitation Chemistry

Transition Metals Elements Definition List Properties Transition Metal Electron Configuration Ionization Energy

Lesson Explainer Electronic Configurations Of Transition Metals Nagwa
Transition Elements General Properties And Trends With Faqs

Important Compound Of Transition Elements In 2022 Transition Element Electron Configuration Binding Energy

Periodic Table Definition Elements Groups Charges Trends Facts Periodic Table Of The Elements Periodic Table Periodic Table With Names

Kids Science Periodic Table Of Elements Electron Affinity Periodic Table Chemistry For Kids

All Transition Elements Are D Block Elements But D Block Elements Are Not Transition Qs Study

Transition Elements Definition Properties Trends My Digital Kemistry Transition Element Element Chemistry Chemistry

Transition Metals Periodic Table Youtube

General Properties Of Transition Elements D Block Videos Examples

The Periodic Table Transition Metals Video Khan Academy

Transition Metals And Their Properties Matter Chemistry Fuseschool Youtube

Difference Between Group 1 Metals And Transition Metals Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
Difference Between Transition Metals And Inner Transition Metals Definition Properties In Relation To Electronic Configuration
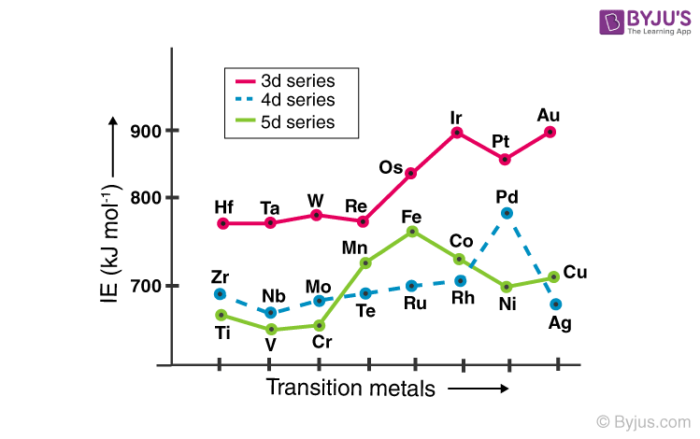
Transition Elements General Properties And Trends With Faqs

Electronic Configuration And General Properties Of D Block Elements Or Transition Elements Online Science Notes

Comments
Post a Comment